JPF Boot Library
Introduction
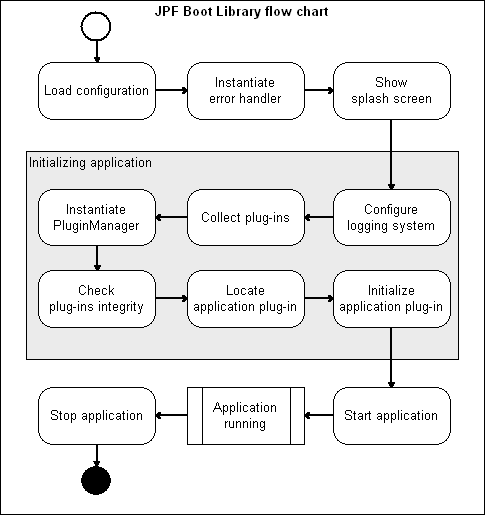
Running JPF based application is often routine and it might be quite tricky, especially for Java beginners. What application developer usually need to do to start (and stop) JPF based application?
- load application configuration
- collect available plug-ins
- instantiate and initialize JPF runtime
- publish (load) collected plug-ins
- activate and "run" main plug-in
- on application exit, properly shutdow Framework
As you can see, this is quite general and common procedure. All steps are usual and good formalized. So it is possible to write some library once and use it again and again for one particular purpose - load, configure and start application. That is the JPF Boot Library (and slightly more as usual :).
Usage
The library packaged in separate JAR file jpf-boot.jar There are special entries placed in manifest of this file that tells JVM what other libraries required for this JAR (jpf.jar so far) and what class to start when running JAR - org.java.plugin.boot.Boot This simplifies library usage and allows to start application simply typing in command shell:
java -jar lib/jpf-boot.jar
Here is typical folders structure:
[APPLICATION_HOME_FOLDER]/ +- lib/ | +- commons-logging.jar | +- jpf.jar | +- jpf-boot.jar | +- log4j.jar +- plugins/ +- boot.properties +- log4j.properties +- run.bat +- run.sh
Put your plug-ins in plugins folder and execute run script. All start up magic will be done by library.
You may remove log4j.jar and log4j.properties files if you don't need logging facilities. See JPF Boot Library javadoc for configuration options.
Look at JPF-Demo application to get working example of JPF Boot library usage.
